KINtaro Database
FAMILY: FAM69 (PKLF000030)
Description
FAM69 kinase domain inlcudes five human genes (FAM69A, FAM69B, FAM69C, C3ORF58 (DIA1), and CXORF36 (DIA1R)). This family remain largely uncharacterized at the molecular level, they have been linked to several neurological disorders in genetics studies. The C3ORF58 gene has been found to be deleted in cases of autism and is known to reside in the Golgi. FAM69 proteins exhibit an unusually high cysteine content. Additionally, an EF-hand Ca(2+)-binding domain found in FAM69A and FAM69B, inserted within the structure of the kinase domain, suggests that they may function as Ca(2+)-dependent kinases [PMID: 23840464].
Origin
phmmer: 0.0001;
database: nr;
sequence_cutoff: 100aa;
clustering: cdhit: 90%;
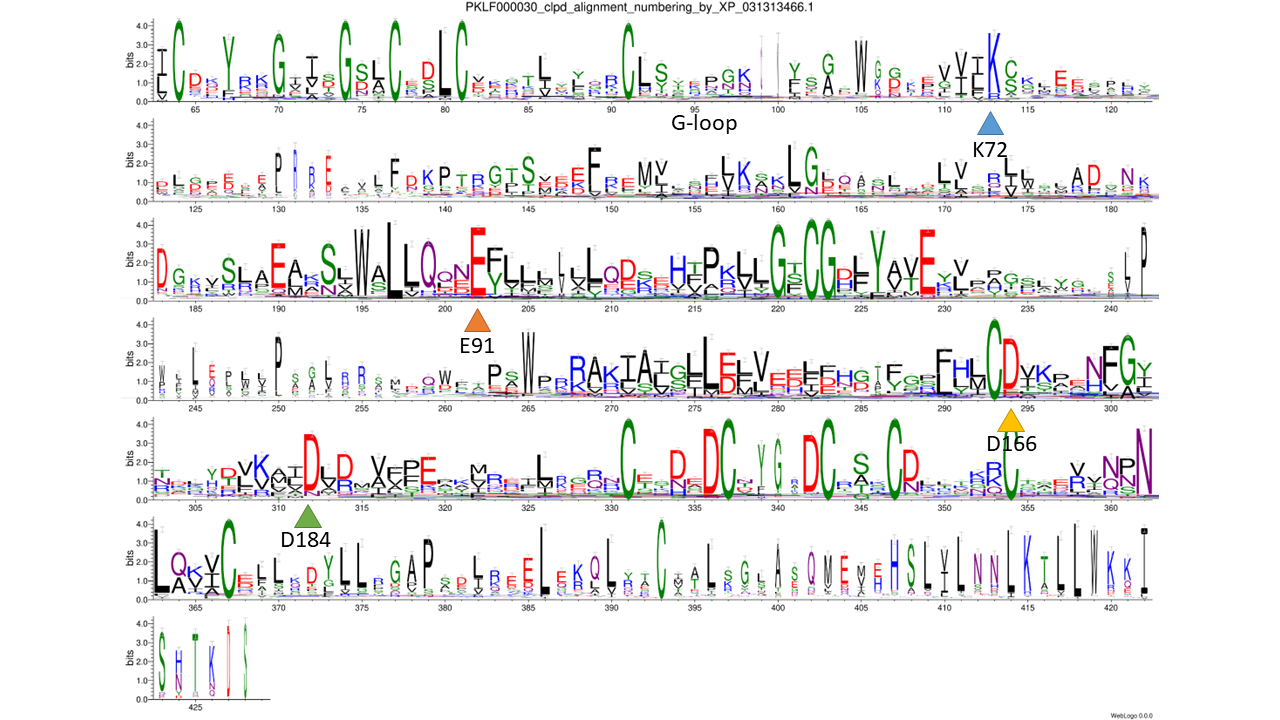
catalytic residues: based on - collapsed family logo, 3D structure model, FATCAT structural pairwise alignment with 1ATP, 1O6Y and 6PWD, PMID: 21334309
HMM Model
WebLogo
 ×
×
![]()
Sequences
Aligned domain sequences
Download sequence
Unaligned domain sequences
Download sequence
Full sequences
Download sequence
Description
FAM69 kinase domain inlcudes five human genes (FAM69A, FAM69B, FAM69C, C3ORF58 (DIA1), and CXORF36 (DIA1R)). This family remain largely uncharacterized at the molecular level, they have been linked to several neurological disorders in genetics studies. The C3ORF58 gene has been found to be deleted in cases of autism and is known to reside in the Golgi. FAM69 proteins exhibit an unusually high cysteine content. Additionally, an EF-hand Ca(2+)-binding domain found in FAM69A and FAM69B, inserted within the structure of the kinase domain, suggests that they may function as Ca(2+)-dependent kinases [PMID: 23840464].
Origin
phmmer: 0.0001; database: nr; sequence_cutoff: 100aa; clustering: cdhit: 90%; catalytic residues: based on - collapsed family logo, 3D structure model, FATCAT structural pairwise alignment with 1ATP, 1O6Y and 6PWD, PMID: 21334309
HMM Model
WebLogo
