ART Database
CLADE: H-Y-E (ARTC000002)
FAMILY: Arr-ms (ARTF000005)
Description
Bacterial ADP-ribosyltransferase family. Mycobacterium smegmatis is resistant to rifampin due to the presence of the chromosomally encoded ADP-ribosyltransferase rifampicin (Arr-ms). Arr-ms is a small enzyme whose activity renders rifamycin antibiotics ineffective.
InterPro - IPR021975
Arr enzymes catalyze ADP-ribosylation of rifamycins, thus rendering rifamycin antibiotics ineffective. The opportunistic pathogen Mycobacterium smegmatis possesses a chromosomally encoded rifampin ADP-ribosyltransferase (Arr-ms). An homologue of Arr, Arr-2, is present in several transposons and integrons found in Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria. The structure of Arr-ms reveals similarity to protein ADP-ribosyltransferases, despite a lack of amino acid sequence similarity [PUBMED:18349144].
WebLogo
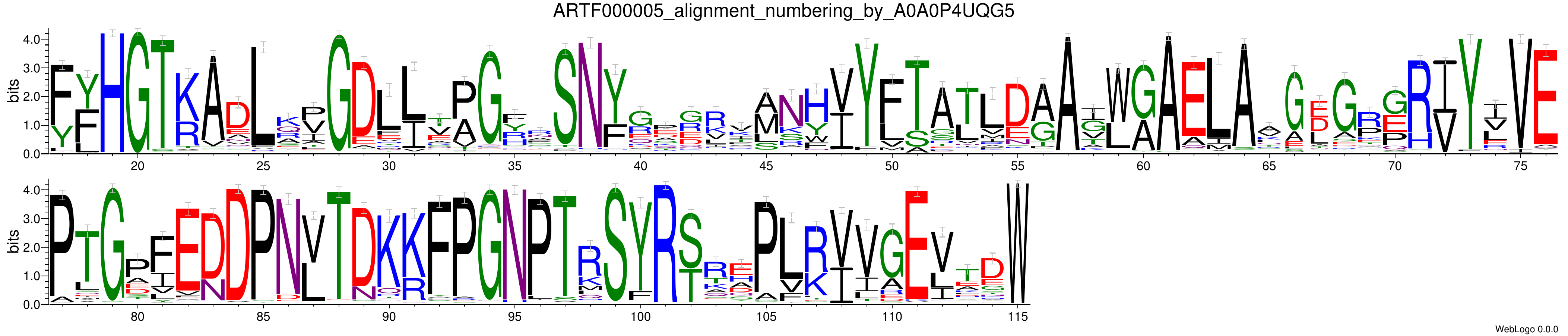
Sequences
Aligned domain sequences
Download sequenceUnaligned domain sequences
Download sequenceFull sequences
Download sequenceHMM Model
Origin
Source: Pfam 34.0, rp75 Number of sequences: 320 Average length of the domain: 99 aa HMM: Model length: 100 Clustering level: 80% Alignment: ClustalO Additional information: sequences longer than 50 amino acids